Published on
Tuesday, September 15 2020
Authors :
Elizabeth Hilbourn
Both California and Oregon have had low carbon fuel programs for several years now. The California Air Resource Board (CARB) identified the Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) as one of nine items under the AB32 Scoping Plan, approved the LCFS regulation in 2009 and began implementation on January 1, 2011. In 2009, the Oregon Legislature passed HB 2186 authorizing the Environmental Quality Commission (EQC) to adopt a low carbon fuel standard to reduce the carbon intensity, or lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions per unit of energy, of Oregon’s transportation fuels. The Oregon Clean Fuels Program (CFP) copies much of its program from California’s LCFS and was implemented in 2016. In fact, if California approves an entity’s pathway, Oregon allows the same GREET 3.0 simplified calculator with simply a transportation adjustment. With that said, it is interesting to note the draw of low carbon transportation fuels to both states.
Table 1 makes an overall comparison of California’s LCFS to Oregon’s CFP. Both programs aim to reduce the average carbon intensity in the state’s transportation fuels by 20% by 2030. CARB approved the new goal in 2018 with their amended regulation. Oregon’s goal changed in 2020 from a 10% reduction in 10 years to 20% by 2030. Pathway validation by approved verification bodies started in January 2020 for California, but not until next year for Oregon. The current credit prices between the two programs also differ. California is, on the most part, drawing its top credit price of $200 per metric ton plus inflation, while Oregon is drawing approximately 75% of that price. Both programs have not veered too much from 10% ethanol in gasoline; however, California’s program has commanded more of the renewables in diesel at 22.9% versus Oregon’s 10.2% while the nation average is still just below 5%.
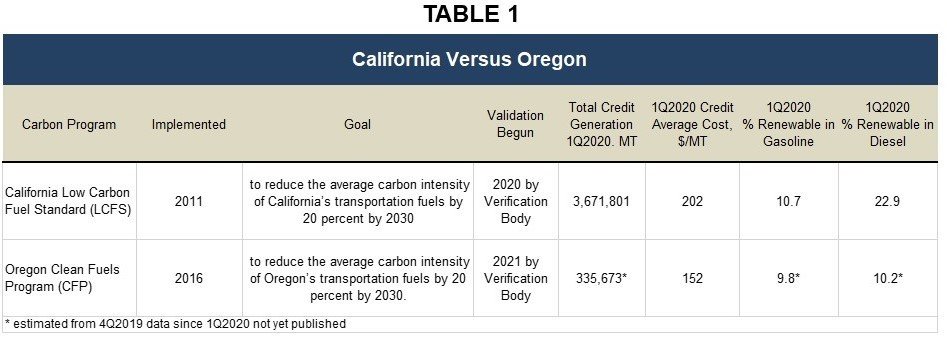
A history of both program’s average monthly credit prices since 2016 is shown in Figure 1. Oregon showed a dip in credit prices at the onset of the coronavirus pandemic in the U.S., but is showing recovery. Overall, Oregon’s credit prices are trending with California’s.
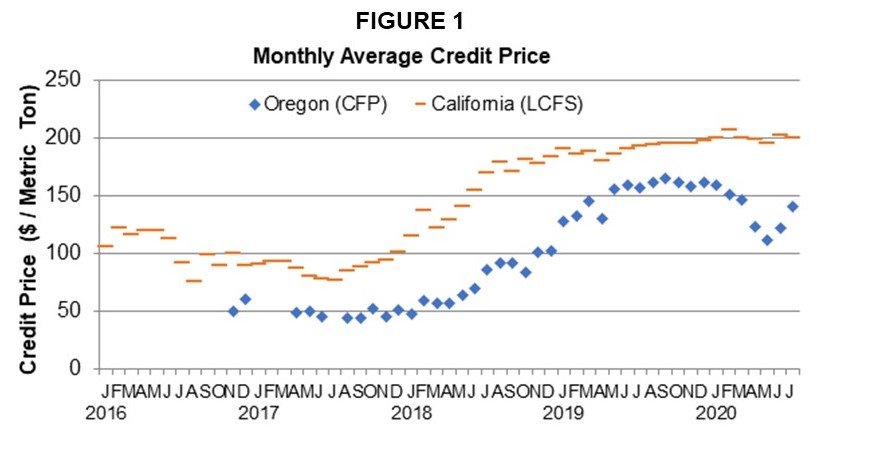
Figures 2 and 3 show the majority of the credit generation since 2016 for both California and Oregon respectively. Overall, California has approximately ten times the amount of credit generation as does Oregon. Oregon has not yet attracted a significant level of biomethane; however, more renewable diesel has entered the market. Oregon mandates 10% ethanol in gasoline and 5% biodiesel in diesel. Overall, Oregon has a higher blend percentage of biodiesel (~8%) than California (~7%) but California blends over twice as much renewable diesel as biodiesel to bring their renewable in diesel to almost 23%. 

Both states offer further incentives to attract renewable fuel production in the states. Oregon, with the Small-Scale Local Energy Loan Program, offers low-interest loans for qualified programs for alternative fuel projects including feedstocks. Property used to produce biofuels, including ethanol and biodiesel, may be eligible for a property tax exemption if it is located in a designated Rural Renewable Energy Development Zone in Oregon. The California Energy Commission (CEC) administers the Clean Transportation Program (Program) to provide financial incentives with the goal of developing renewable fuels.
TM&C Fuels Regulatory Practice has a wealth of experience spanning several decades in virtually all of the clean fuel programs affecting refiners and marketers, and we are now available as a third-party verification body for the California LCFS program and the Oregon Clean Fuels program. Throughout its history, TM&C has provided consultation on EPA and state fuel programs in essentially all aspects of compliance. The “Focus on Fuels” provides a deeper dive into the current regulatory issues facing the industry. If you would like to be included on the distribution list, visit our “Contact Us Page” on our web site and let us know in the message box. Feel welcome to give our regulatory compliance team a call at (214) 754-0898
